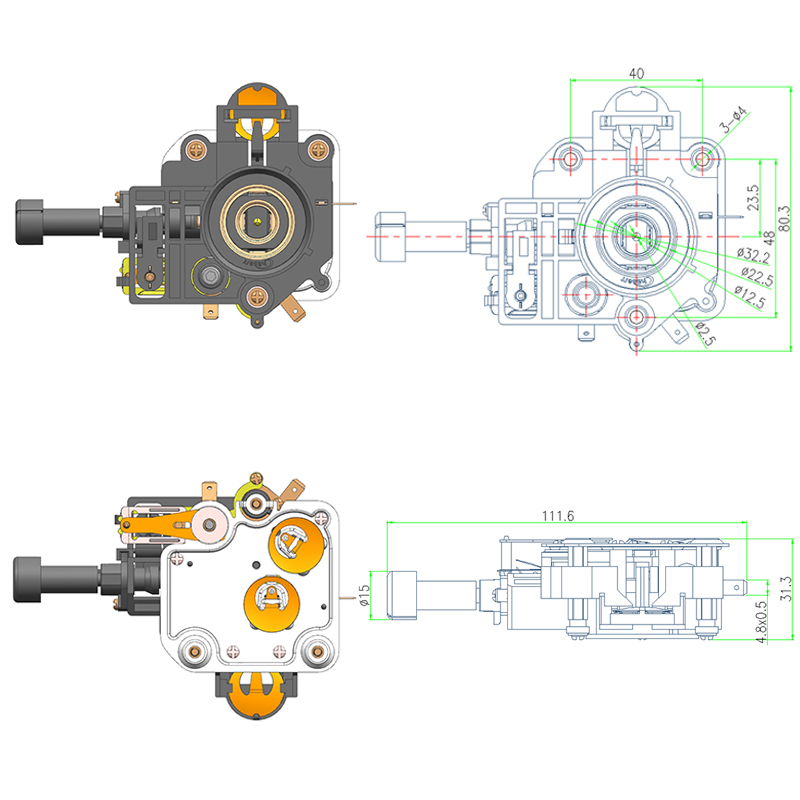
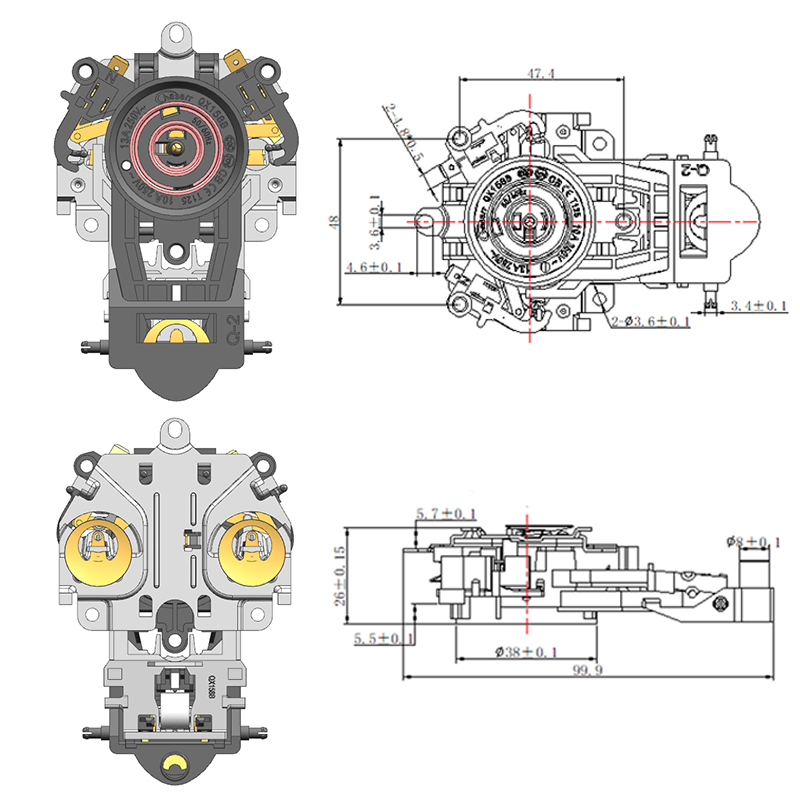
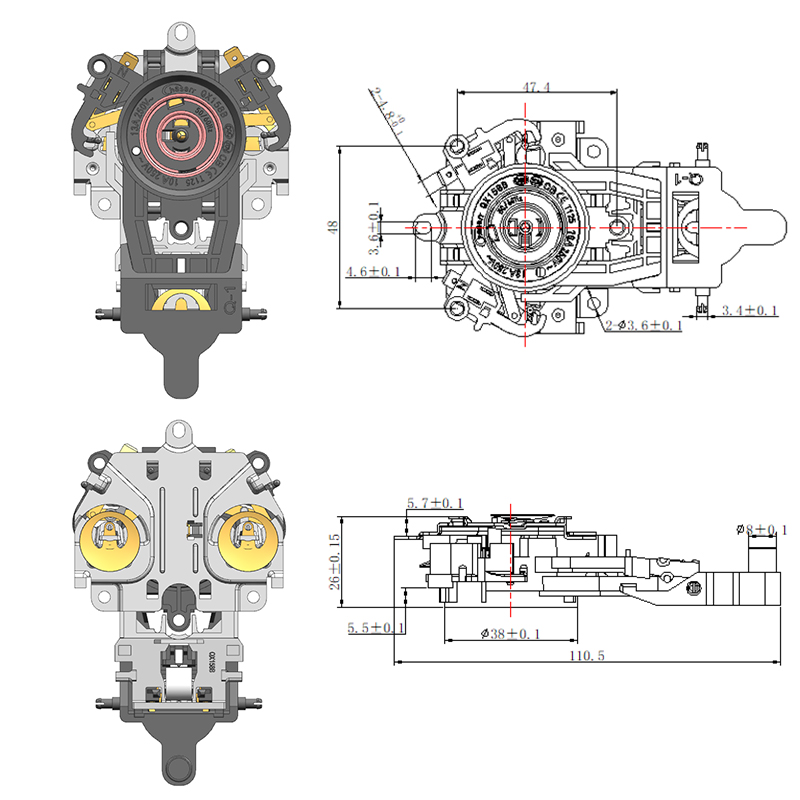
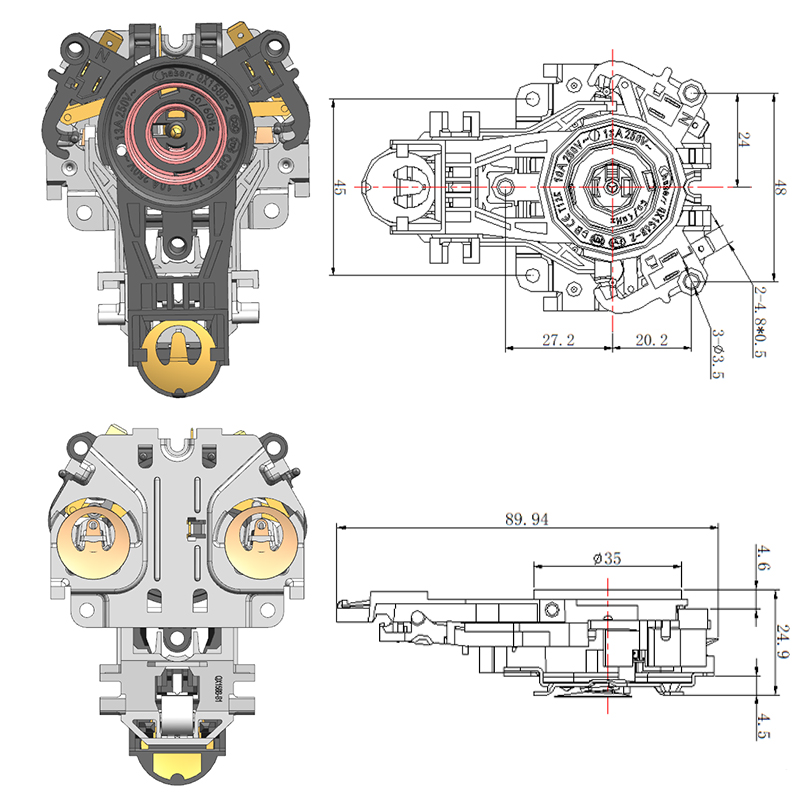
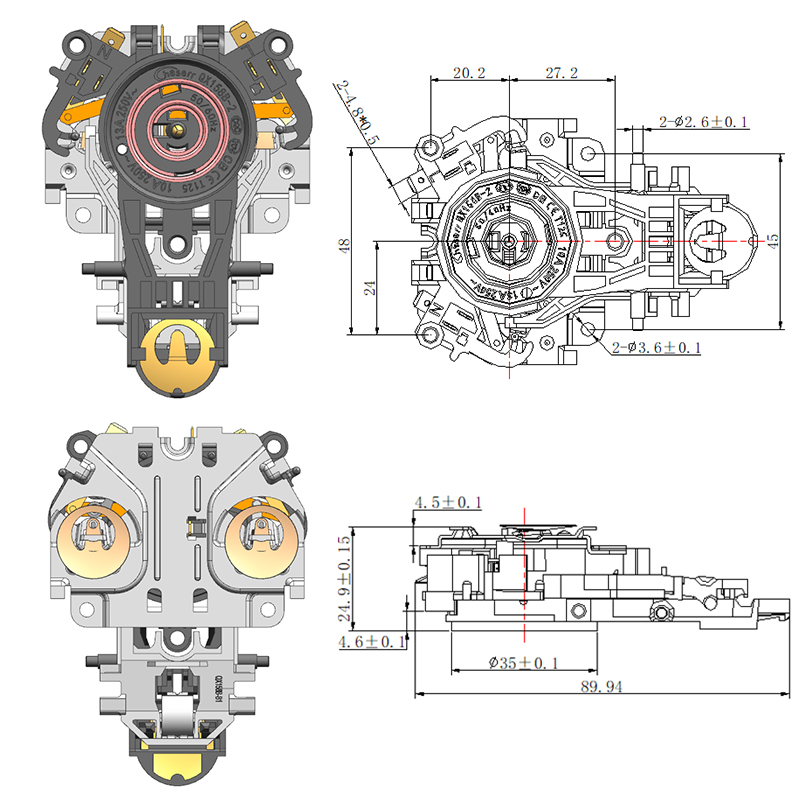
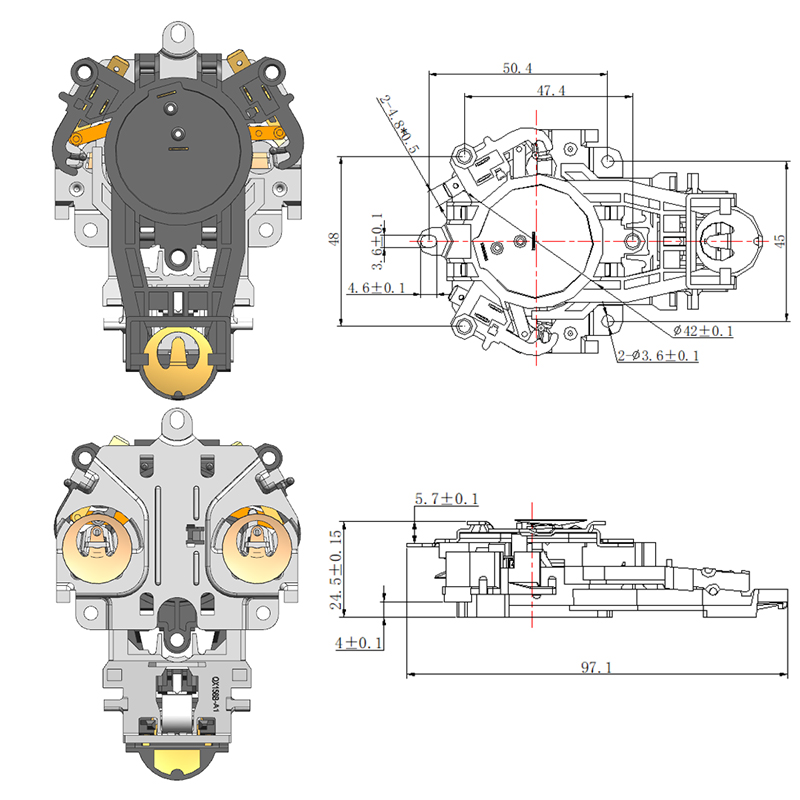
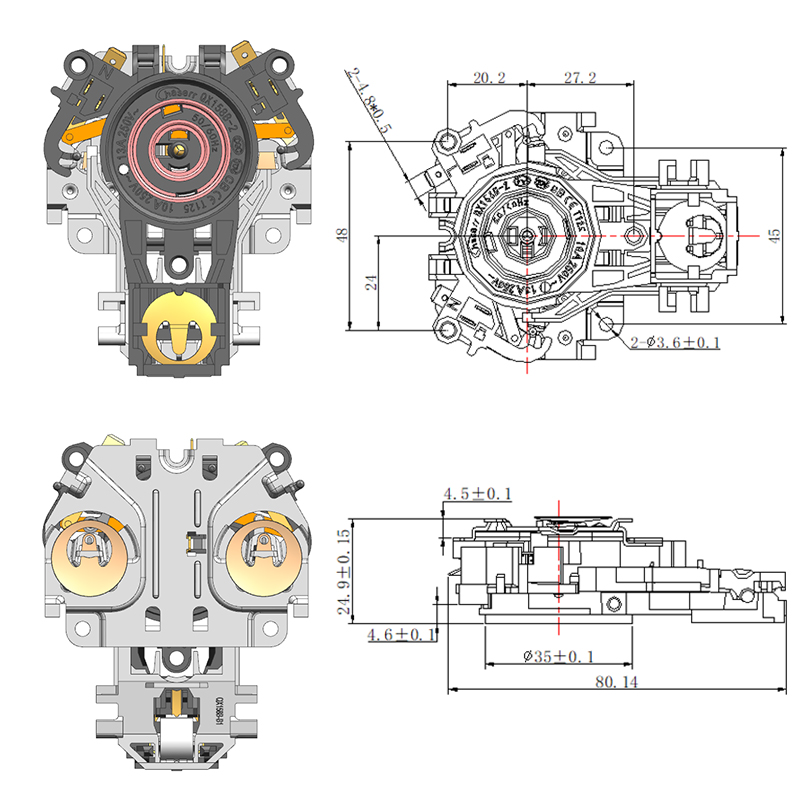
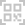Common Design Differences Between a Steam Thermostat and an Electric Control Thermostat
Introduction to Thermostat Functionality in Kettles and Appliances
Temperature control is a fundamental requirement in appliances such as electric kettles, coffee machines, and other heating devices. Thermostats play a key role in managing when these appliances heat up and when they shut off. Among the various types, the Steam Thermostat and the Electric Kettle Control Thermostat are commonly used for different design purposes. Although both serve to regulate temperature, their operational principles, components, and control mechanisms differ in several important ways.
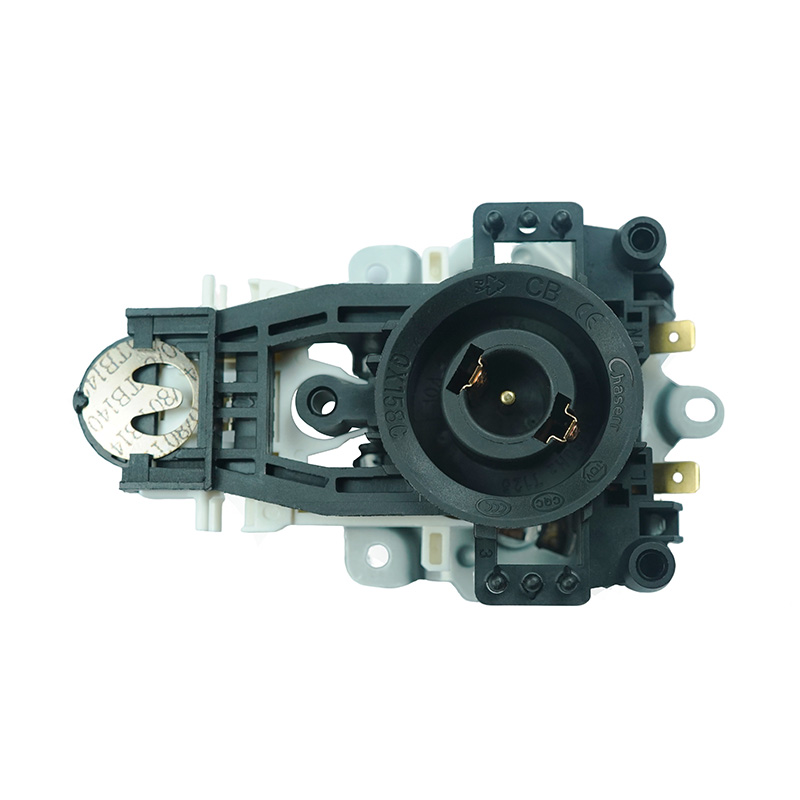
Working Principles of Steam-Based Thermostats
A Steam Thermostat functions primarily by detecting the presence of steam generated from boiling water. This type of thermostat is often found in traditional electric kettles. It typically includes a sensor positioned near the spout or steam exit path. As water begins to boil, steam travels up a dedicated channel and heats a bimetallic strip or thermal sensor, which then reacts to the increase in temperature and triggers the kettle to switch off. This indirect method of temperature detection provides a reliable way to sense the end of the boiling process without needing direct water contact.
How Electric Control Thermostats Operate
In contrast, an Electric Kettle Control Thermostat relies on direct temperature feedback from a sensor in contact with the heating plate or water chamber. This type is usually more advanced and is capable of detecting a wide range of temperatures, allowing the user to select different heat levels for various purposes such as brewing green tea, coffee, or boiling water. Unlike the steam-based version, the electric control system monitors real-time temperature changes through electrical resistance or digital sensing, providing more precise control over heating cycles.
Physical and Structural Differences
The Steam Thermostat is generally a simpler mechanical device that operates without complex electronics. Its construction typically involves fewer components, making it compact and cost-effective. These thermostats often have a snap-action mechanism activated by heat from steam, which toggles the power state of the appliance.
On the other hand, the Electric Kettle Control Thermostat is part of a more sophisticated setup. It includes integrated sensors, circuitry, and often works in conjunction with microcontrollers. This design allows for multiple temperature presets, keep-warm functions, and more accurate timing. As a result, the overall build is more complex and typically requires larger housing and additional insulation.
Precision and Application Range
In terms of application, the Steam Thermostat is well-suited for appliances where a simple on-off boiling function is required. Its design ensures that the appliance turns off shortly after reaching 100°C, which is ideal for basic water boiling needs. However, it cannot maintain or modulate different temperature levels.
The Electric Kettle Control Thermostat, on the other hand, is favored in appliances that need variable temperature settings. It allows precise adjustments for different brewing requirements and is essential in high-end or programmable electric kettles. This versatility makes it ideal for users who demand flexibility in temperature control.
Conclusion
Both the Steam Thermostat and the Electric Kettle Control Thermostat serve essential roles in modern heating appliances, but they are built with different technologies and for different use cases. While the former is reliable and ideal for basic boiling applications, the latter offers greater precision and functionality for more advanced user preferences. Understanding these design differences helps manufacturers and users select the right thermostat technology based on performance needs, cost, and user experience expectations.
 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  Español
Español