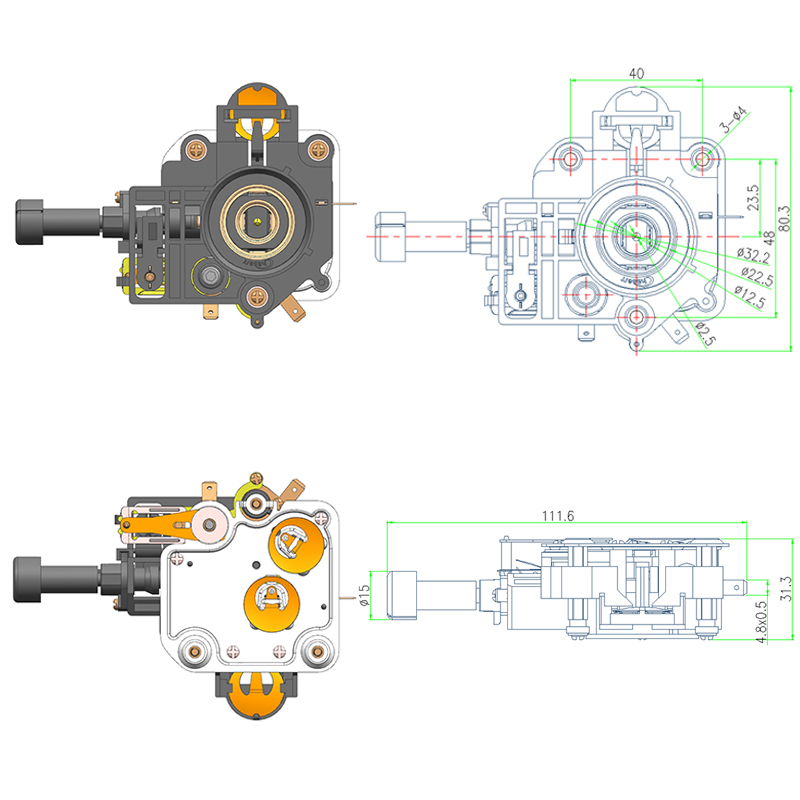
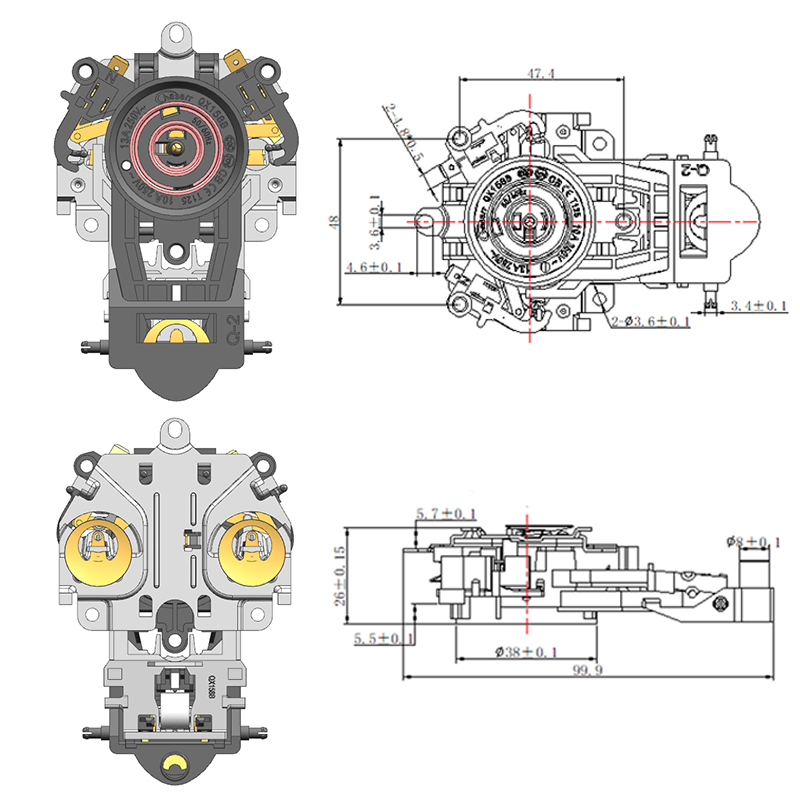
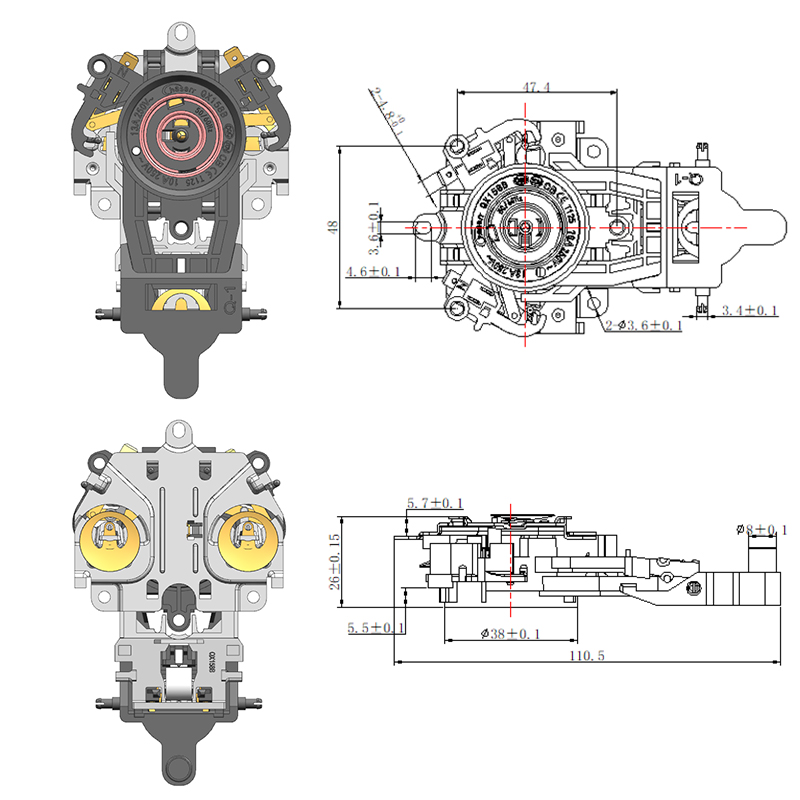
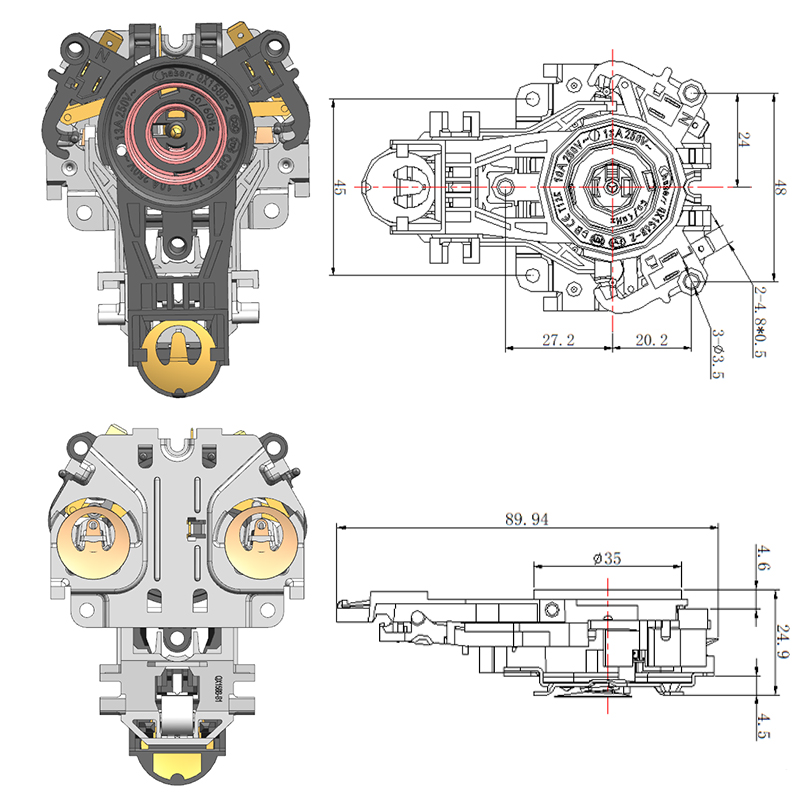
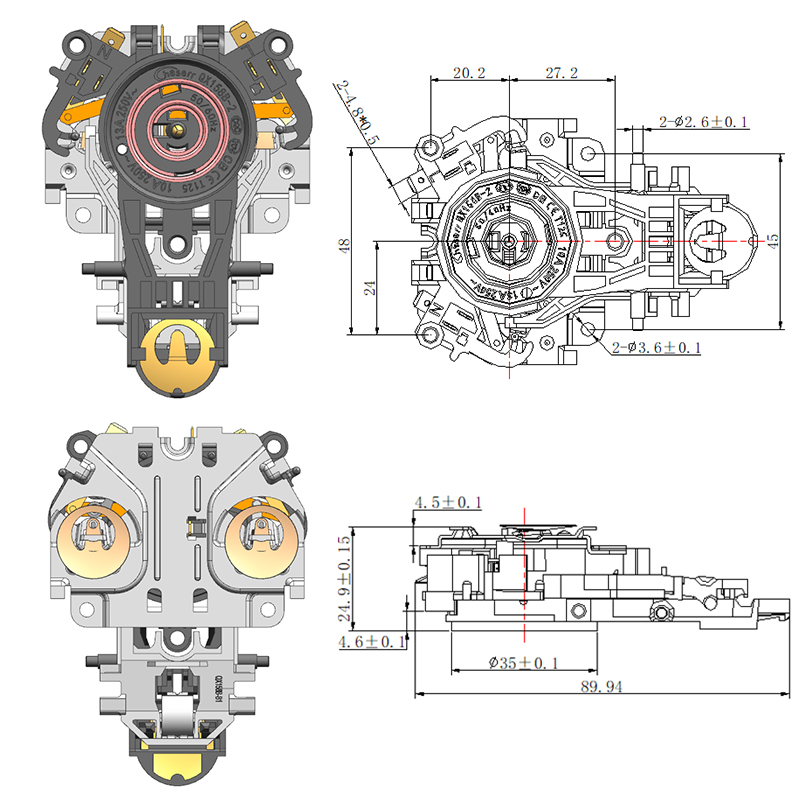
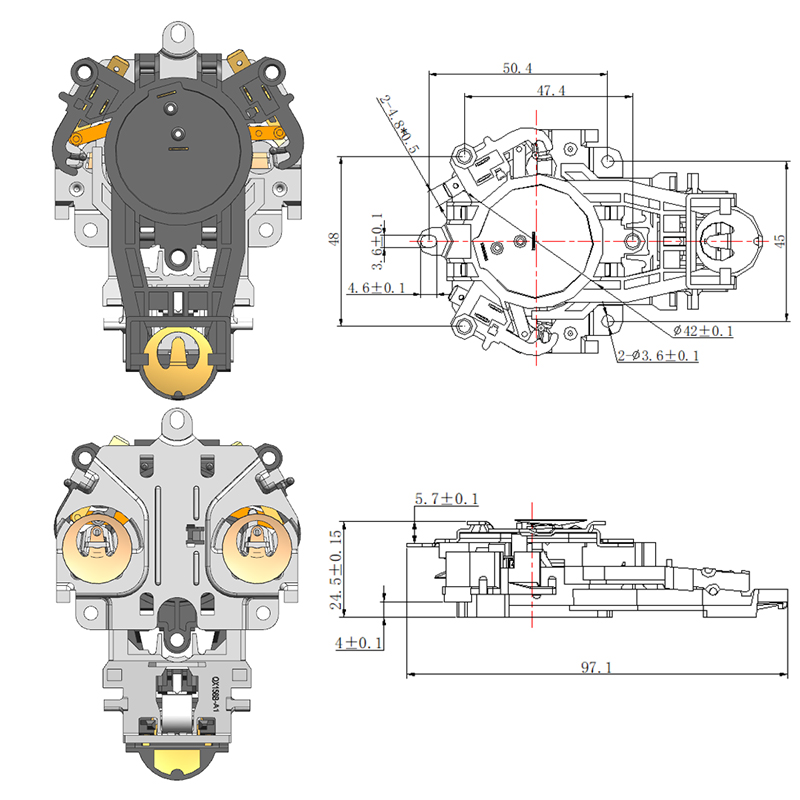
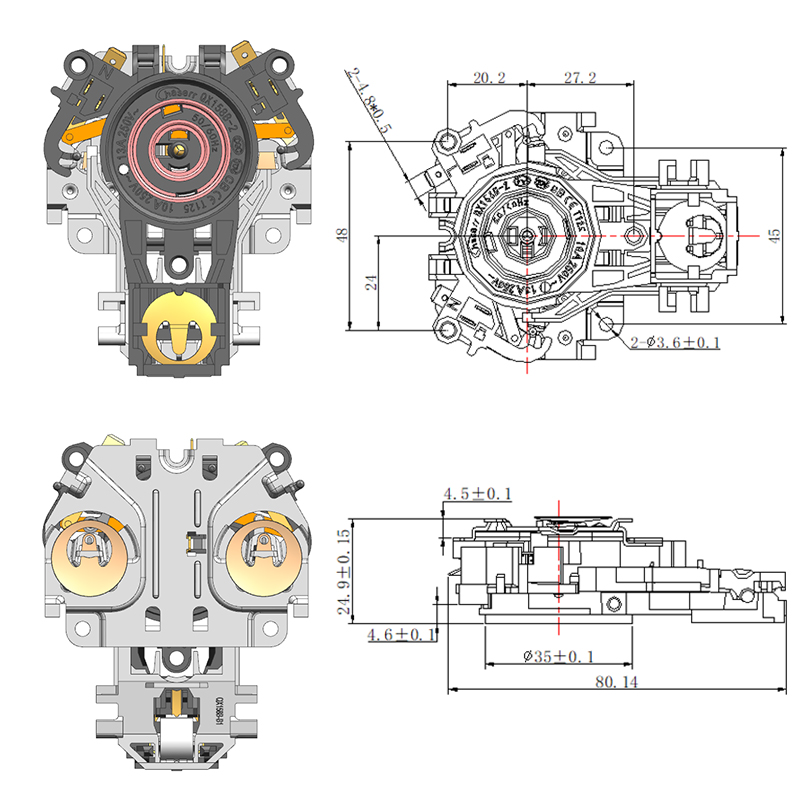
Structural Materials Commonly Used in Manufacturing a Durable Electric Kettle Bottom
High-Temperature Resistant Plastics for Outer Housing
One of the commonly used materials in the outer structure of an electric kettle's bottom is high-temperature-resistant plastic. This plastic serves multiple purposes: it provides a protective shell for the internal components, maintains user safety by acting as an insulator, and withstands thermal cycling caused by repeated use. Polymers such as polypropylene (PP) and polyphenylene oxide (PPO) are popular choices because of their good resistance to deformation under heat. These materials are also lightweight and cost-effective, which helps manufacturers produce kettles at competitive prices without compromising performance.
Stainless Steel Components for Conductivity and Heat Dissipation
While the outer shell of the electric kettle bottom is typically made from plastic, key internal components may include stainless steel. Stainless steel is often used in the support plate, contact points, and in some cases, the inner lining of the base. It offers several advantages, including corrosion resistance, high thermal conductivity, and mechanical toughness. Its ability to conduct heat evenly makes it a valuable material, especially in advanced kettles that feature precise temperature control.
Some kettles, especially those that include a smart hot water kettle thermostat, require better heat management around the sensor area. In such designs, stainless steel is sometimes strategically positioned to help distribute heat more predictably, ensuring accurate readings by the thermostat.
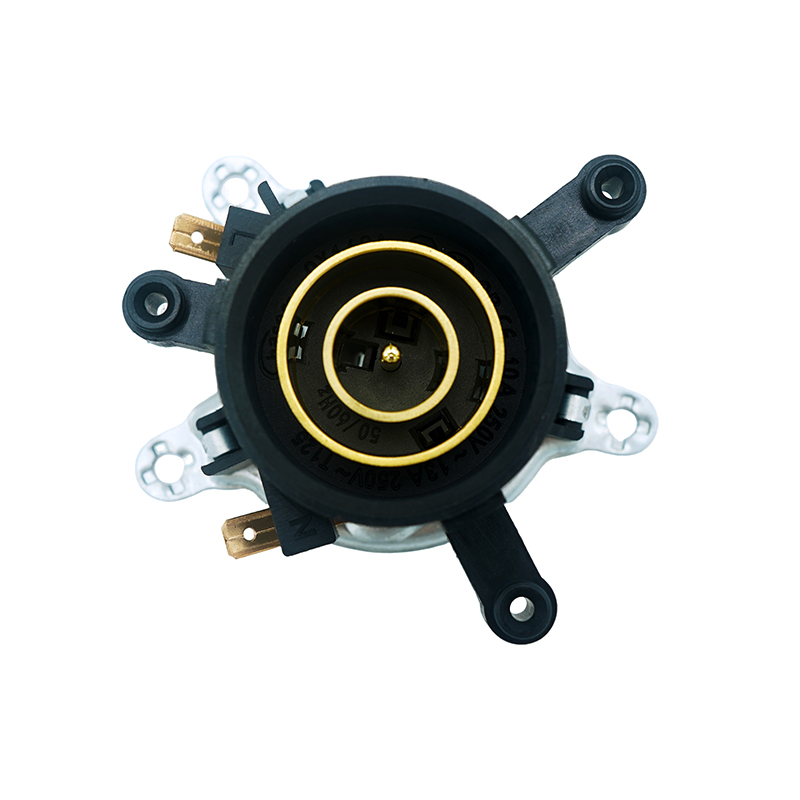

Silicone and Rubber Elements for Sealing and Vibration Damping
In addition to rigid materials, flexible components like silicone and rubber are used in certain areas of the base assembly. These materials serve as gaskets, seals, or vibration dampers. Their primary function is to ensure that no water or steam enters the internal electronics, which is crucial for both safety and function. Silicone, in particular, is favored due to its resistance to high temperatures and long-lasting flexibility.
Flexible materials also contribute to noise reduction and smoother user interactions. For instance, the addition of a rubber ring at the base interface can reduce clanking sounds when the kettle is placed or removed. In systems incorporating a smart hot water kettle thermostat, silicone seals are even more critical as they prevent moisture from interfering with the electronic sensors.
Copper and Brass for Electrical Contacts
Within the kettle base, electrical contacts are crucial for transferring power from the base to the kettle. These contacts are usually made from copper or brass due to their good electrical conductivity. These metals ensure that electricity flows efficiently, with resistance or heat buildup. Copper, while softer, is highly conductive and often used with protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Brass offers a good balance between conductivity and durability, making it a popular choice for rotational connectors and spring contacts.
Conclusion
The durability and performance of an electric kettle's bottom depend heavily on the materials selected for its construction. From high-temperature plastics to stainless steel and conductive metals, each material serves a specific purpose in enhancing the kettle's longevity and safety. As innovations continue, especially with the rise of the smart hot water kettle thermostat, new materials and design refinements are being introduced to meet higher performance demands. Understanding these material choices not only sheds light on how kettles function but also highlights the complex engineering behind everyday appliances.
 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  Español
Español