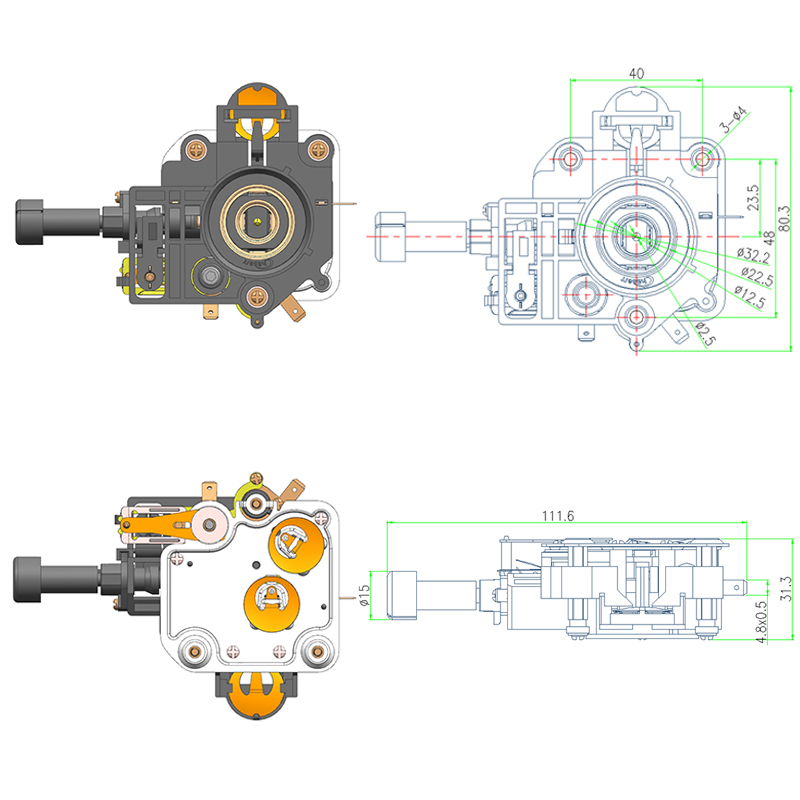
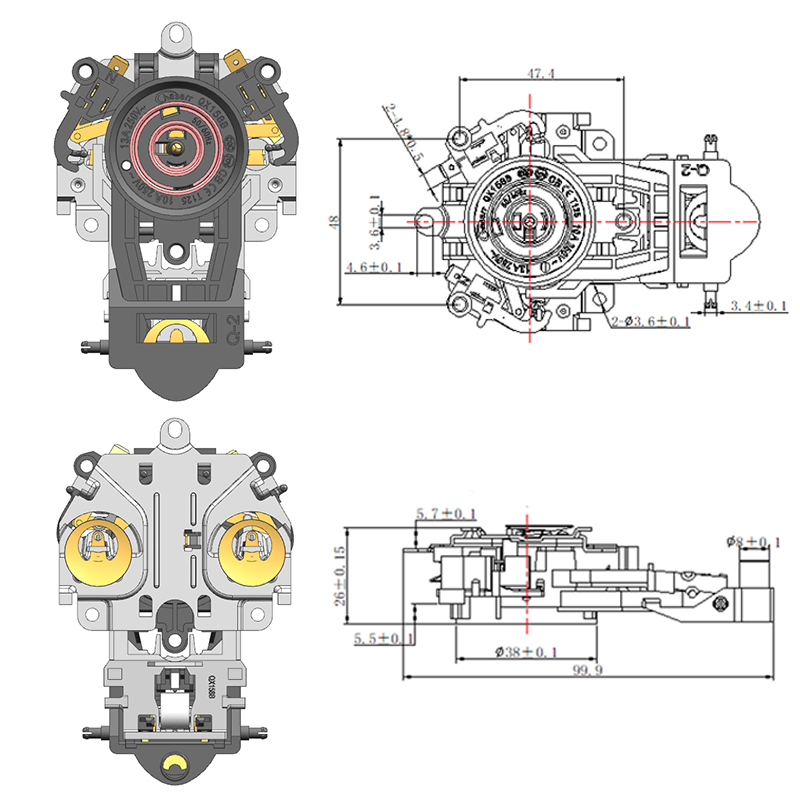
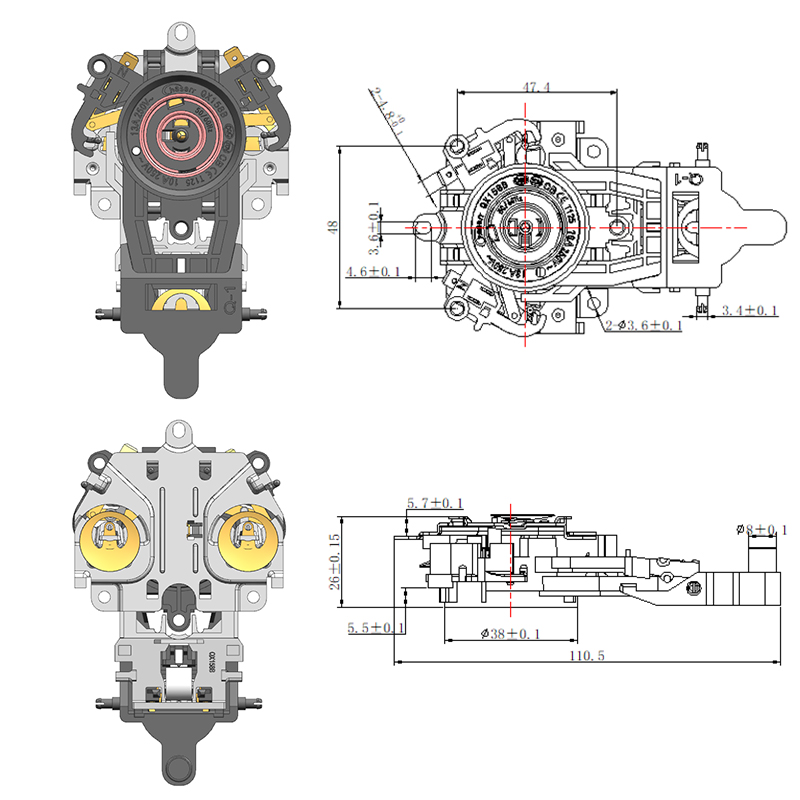
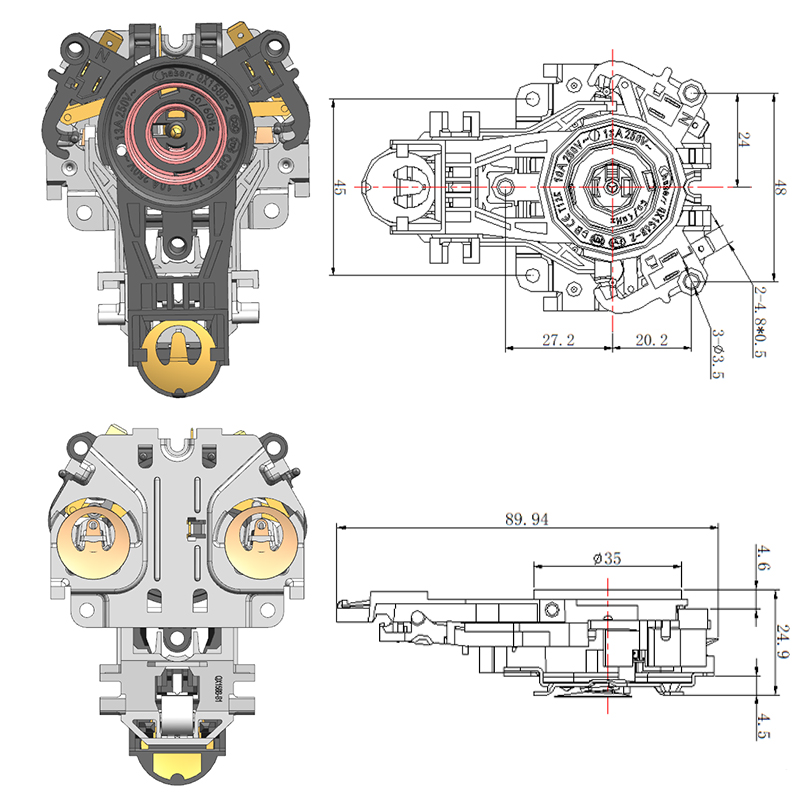
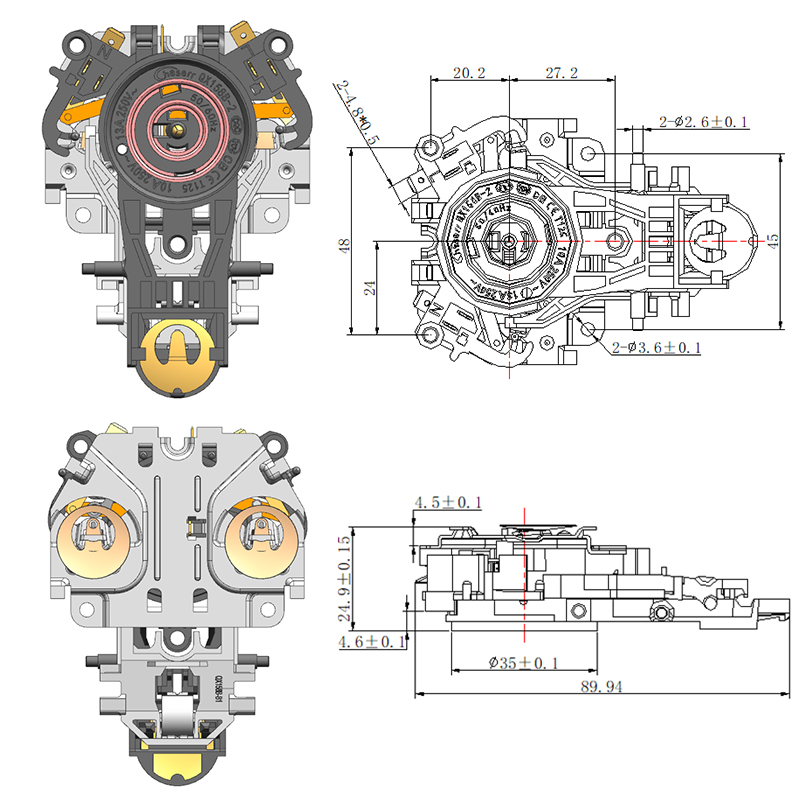
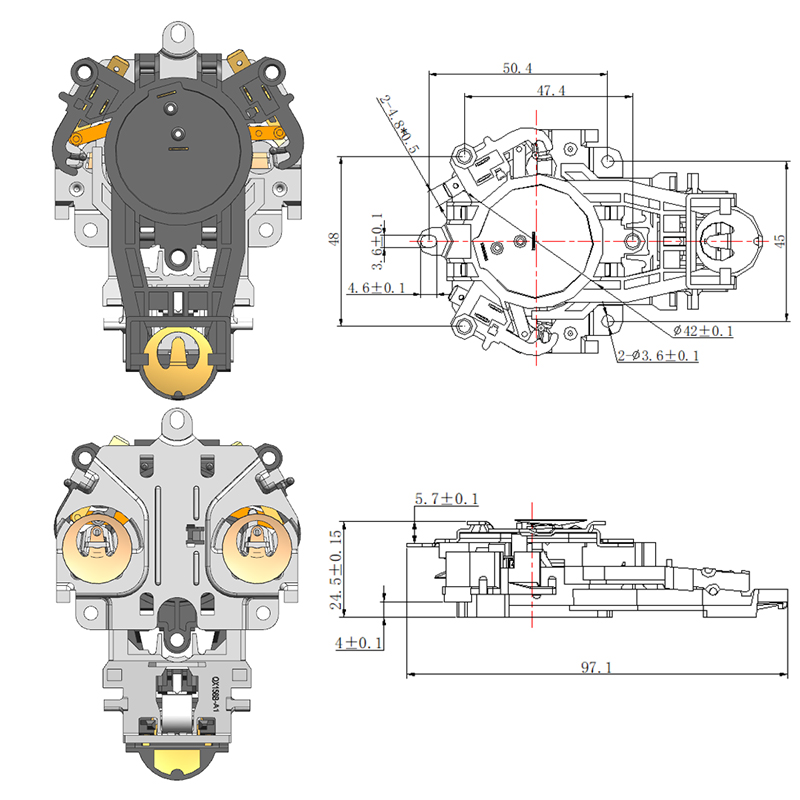
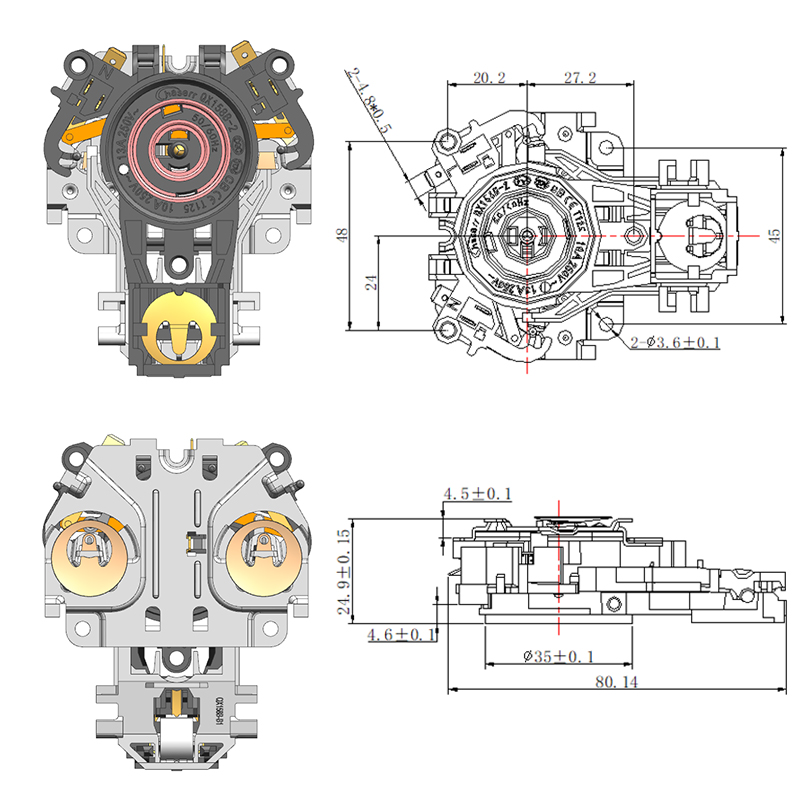
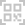Importance of a Stable Thermostat Base in Ensuring Accurate Sensor Performance
The Foundation of Reliable Temperature Control
Accurate temperature measurement is essential for effective heating and cooling systems. At the heart of this accuracy lies the Thermostat Base, which serves as the physical foundation for the sensors within various thermostat devices. Without a stable and well-designed base, the sensors can provide incorrect readings, causing inefficiency, discomfort, or even safety issues. This is particularly true in modern devices such as the Water Ring Smart Thermostat and the Adjustable Temperature Thermostat, where precise control is vital for suitable performance.
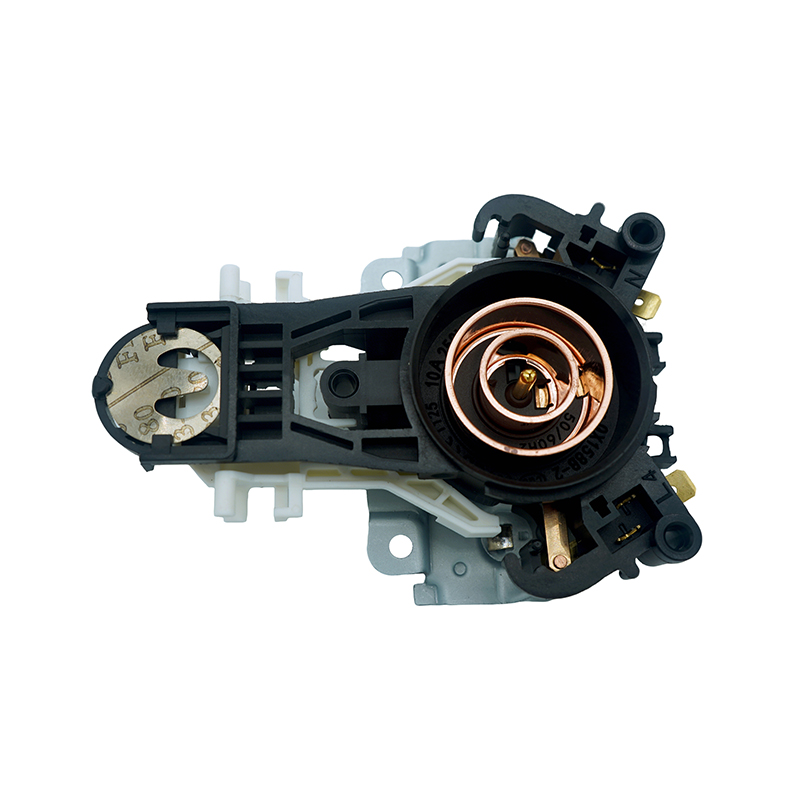

How Stability Affects Sensor Accuracy
The Thermostat Base must hold sensors firmly in the correct position to ensure they accurately detect the ambient temperature. Any instability, such as wobbling or shifting, can cause the sensors to misread temperatures. Even slight movements can introduce errors by exposing sensors to heat sources or drafts that they are not intended to measure. For smart systems like the Water Ring Smart Thermostat, which relies on precise data to optimize energy consumption and user comfort, sensor misalignment can reduce the effectiveness of the entire system.
Material and Design Considerations for the Thermostat Base
The choice of materials and structural design for the thermostat base greatly impacts its stability. High-quality plastics or metal alloys are commonly used for their durability and resistance to temperature fluctuations. The base should be rigid enough to resist deformation from mounting or environmental stress. Additionally, the design must accommodate secure installation, whether on a wall or device housing, to prevent unwanted motion.
In the case of the Adjustable Temperature Thermostat, users expect consistent and repeatable temperature control. A robust thermostat base helps maintain sensor integrity over time, avoiding performance degradation caused by loosening or wear.
Impact on Adjustable Temperature Thermostat Performance
Devices with adjustable temperature settings require constant and accurate sensor feedback to maintain the desired temperature. An unstable base can cause frequent fluctuations and inaccurate readings, causing the system to overheat or underperform. This results not only in discomfort but also in increased energy consumption and potential strain on heating or cooling equipment.
A well-engineered thermostat base ensures that the sensors remain correctly positioned throughout the device's lifespan, supporting the precise functionality users demand from adjustable thermostats.
Benefits of Water Ring Smart Thermostat Systems
The Water Ring Smart Thermostat integrates intelligent features such as remote monitoring, scheduling, and adaptive learning based on sensor input. For these functions to work effectively, sensor data must be accurate and reliable. The thermostat base plays a crucial role in stabilizing sensor placement, reducing errors caused by vibration or improper installation.
By providing a stable platform, the thermostat base enhances the performance of smart control algorithms, causing improved energy efficiency and a better user experience. Without a secure base, the advantages of smart thermostats would be compromised by unreliable sensor data.
Conclusion
The stability of the Thermostat Base is fundamental to the accurate performance of sensors in both traditional and smart temperature control devices. Whether in an Adjustable Temperature Thermostat or a sophisticated Water Ring Smart Thermostat, a well-designed base ensures sensors remain correctly positioned and reliable. This stability directly affects temperature accuracy, energy efficiency, and user comfort. Manufacturers and consumers alike should recognize the importance of a stable thermostat base as a critical factor in achieving consistent and effective temperature regulation.
 English
English  中文简体
中文简体  Español
Español